
Held in TUESDAY 15TH MARCH 2022
Agrilife24.com:BETTER PHARMA (International Animal Health Business) together with Prof. Dr. Thaweesak Songserm DVM, PhD. recently, an online virtual seminar was held to suit the situation in the very important topic How to fight with the right solution? "Poultry Diarrhea & Wet Dropping”. There are interested parties who attended at that time including at least 4 countries Bangladesh, Vietnam, The Philippines, Indonesia, and most of the participants were veterinarians, animal husbandries and nutritionists. In that time seminar, participants were given from the speaker's perspectives which can be summarized in a holistic way as follows:
GUT: ECOSYSTEM WITH COMPLEX & HIGH CAPABILITY
• Genetic selection for rapid growth in commercial poultry leads to dramatic adaptation of the gut in order to achieve fast growing.
• Gut plays highly important role in growth, homeostasis and balancing body and environment.
• Microorganisms, organic materials (feed and eatable materials), hormone, blood, electrolytes, immune components, etc. present, live and work as a networking.
• Interaction of these components directly impact on health status of gut.
• Gut has many functions, like Industrial estates.
• Big challenge!!! How to maintain this ecosystem in sustainable of good condition (structure and functional).
- Microbiome = Microorganisms and their genes living in a specific environment.
- Microbiota = Microorganisms (by type) living in a specific environment (Taxonomy of presented microorganisms).
- Metagenome = The genes of microorganism in a specific environment (collective functions of microorganisms’ genes).
- Normal flora = A subset of microbiota.
GUT MICROBIOTA
• At hatch, chicks’ gut already receive microbiota from environment such as hatchers, hatchery room.
• The microbiota is colonized in the gut with a big variety of strains though they are not brought from the hen mother (vertical transmission). At houses, they come from feed, water, litter and others, or oral-fecal contaminants (from other birds like pigeons and house sparrows).
• This microbiota gradually increase number, depending on micro environment at that time and age of chickens.
MECHANISM OF GUT CONTROLLING PATHOGENS
• Structure, physiology, and environment of enteric system.
• Competition for enteric attachment sites.
• Competition with the host and other microbes for nutrients.
• Production of antimicrobial compounds or agents such as bacteriocins and bacteriophage.
• Immune stimulation.
THE ROLE OF GUT MICROFLORA IN PROTECTION OF PATHOGENIC AGENTS
• Competition for binding sites.
• Competition for nutrients.
• Production of antimicrobial substances.
• Immune stimulation.
WHAT HAPPENS IF GUT IS NOT IN GOOD CONDITION AND FUNCTION?
• Gut itself adapt and balance in function, depending on how serious the bad condition is.
• If gut is under more serious and progressive problem, its structure and function become worsen and finally stops working and may distribute the problem to other organs.
• Clinical/subclinical problems often result in growth retardation, economic loss, death and probable carcass condemnation.
• Mucosal immunity is unable to function properly. Furthermore, leading to immunosuppression and subsequently complicated infection.
• Fail to maintain homeostasis in the body.
INGESTION, DIGESTION, ABSORPTION, FERMENTATION AND EXCRETION
- Oral cavity and its accessory organs are important to gain the feed. Any lesions found in oral cavity mostly directly impact on feed intake.
- Digestibility of gut is depended on enzymes, gut micro environment, types of feed and mucosal health i.e. gut morphology.
- Absorptive areas with efficient function lead to optimal growth, especially fast growth breeds. Mucosal lesions result in poor digestion and absorption, subsequently poor growth.
- Normal fermentation (cecum) are worked by a wide variety of microorganism so-called microbiota.
- Excretion of waste products from digestion and absorption.
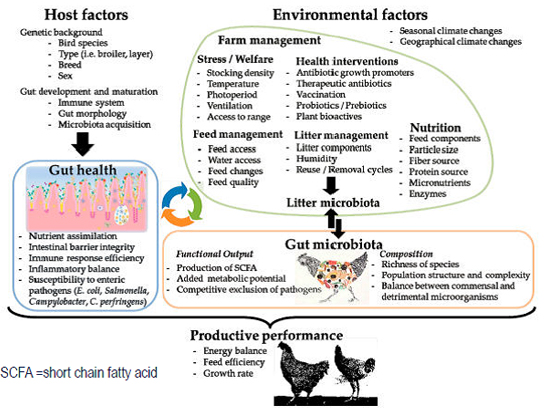
FACTORS INVOLVING GROWTH & FUNCTION OF ENTEROCYTES
- Nutrients and growth promotors.
- Intra GI and extra GI hormones.
- Digestible and non-digestible feed materials.
GUT INTEGRITY (INTESTINAL INTEGRITY) NORMAL MORPHOLOGY/STRUCTURES & FUNCTION:
- Digestibility of feed.
- Capable of nutrient absorption.
- less wastage of nutrients.
- Minimize foul adore.
- Provides resistance against Entero-pathogens.
- Checks mortality and morbidity losses.
- Optimizes feed conversion ratio.
DIARRHEA AND WET DROPPING IN CHICKENS
Non-infectious factors;
- Warm temperature in the houses.
- High level of salts in feed.
- Over non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) in feed.
- High non-digestible protein in feed.
- High total hardness drinking water.
- Mycotoxins contaminated feed.
Infectious factors;
- Enteric reovirus infection.
- Early stage infection of Coccidia.
- Intestinal parasites (round and tape worms).
- Pathogenic enteric bacteria infection (Gallibacterium, Salmonella spp. Fowl cholera, E.coli).
- Biofilm in water pipe line.
Intestinal dysbacteriosis;
- Non-specific enteric disease.
- Adverse imbalance of “good” and “bad” enteric bacteria.
- Still need to be clarified. Dysbacteriosis, the presence of abnormal microbiota in the small intestine, associated with reduced nutrient digestibility, impaired intestinal barrier function, bacterial translocation and inflammatory responses.
BROODING MANAGEMENT PLAYS AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN GUT DEVELOPMENT AND HEALTH
• The faster the chicks eat feed, the more and faster chicks’ gut gets structurally and functionally maturation.
• Suboptimal management and delayed feeding this period results in impaired gut’s development and immunity.
• Inappropriate temperature this period can stress chicks, decreased feed intake, poor development and function of gut.
• Poor feed quality leads poor FCR.
• Fine feed will pass the gizzard faster, resulting in mal-digestion and mal-absorption of nutrients, especially, protein/amino acid.
KEY POINTS TO BALANCE GUT HEALTH OF POULTRY
- Feed and feeding: Feed change, quality of raw materials, toxic & chemical contamination.
- Proper brooding management: The faster the chicks eat feed, the more the gut is developed (morphology and function).
- Eradicating the risk factors: Well prepared housing and management factors, especially biosecurity. Also take care of welfare.
- Good vaccination: Good application and good monitoring uniformity of application.
- Welfare: Being well with normal behavior of poultry.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
- FACULTY OF VETERINARY MEDICINE, KASETSART UNIVERSITY, KAMPHAENGSAEN, THAILAND.
FOR MORE INFORMATIONS
PLEASE CONTACT via our Global email, Facebook and BETTER PHARMA staff.
Mr. Apiwat Wuttinimit
Country Manager - International Animal Health Business
Better Pharma Company Limited, Betagro group, Thailand
Mail : This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. , This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.





















